Trigonometry Definition and formulas
Introduction To Trigonometry
Historical
facts: Hipparchus of Nicaea (190 BC-120 BC). was a Greek
astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of
trigonometry but is most famous for his incidental discovery of p recession of
the equinoxes. Hipparchus, credited with compiling the first trigonometric
table, is known as 'the father of trigonometry' Hipparchus was the first to
tabulate the corresponding values of arc and chord for a series of angles. The
first use of the idea of 'sine' in the way we use it today was in the work
Aryabhatiyam by Aryabhata in AD 500.
Introduction: The word "Trigonometry' is derived from
three Greek words Tri-Gonia-Metron. "Tri' means 'three', 'gonia' means
"an angle' and 'metron' means 'measure, In recent times trigonometry is widely
applied in many branches of Science and Engineer Such as seismology, design of
electrical circuits, estimating the heights of tides in the ocean
Recapitulation:
Angle:
Two rays are intersecting at one common end point is
called an angle.
An angle is usual denoted by A, B. ... etc.
Units
of measurements of angles:
1.The
sexagesimal system :
In this system unit of measurement of an angle is
'degree', Degree : In this system one
Complete rotation is divided into 360 equal parts. Each
parts is called 'a degree',
denoted as 1°. In this system, one right angle is 90°
2. Centesimal
system :
In this system unit of measurement of angle is 'grade'.
Grade: In this system one complete rotation is divided into 400 equal parts.
Each part is called 'a grade', denoted as 1 g. In this system, one right angle
is
3.The
circular system :
In this system unit of measurement of an angle is 'radian'. Radian : The angle subtended by an arc of the length equal to the radius of the circle at its cent re is called one radian, denoted as 1 c.
Note: The
formula connecting the three systems can be stated as D/90=G/100 =2c/π
Where D denotes degrees, G denotes grades and C denotes
radians.
You May Also Read
Mathematics trigonometry Exercise - 11.1
Trigonometric Ratios:
The ratios of sides of a right angled triangle are called trigonometric ratios of angles.
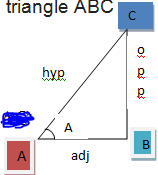
Let ABC be a right angled triangle with right angle at B and angle A is an acute angle.
In a right triangle ABC, the side BC faces the angle A is called opposite side to the angle A,
the side AB is the adjacent side to angle A and AC is the hypotenuse of triangle ABC
1. Sin A = side opposite to angle A / hypotenuse =BC/AC
2. cosine A = cos A = side adjacent to angle A / hypotenuse=AB/ AC
3. tangent A= tan A=side opposite to angle A /side adjacent to angle A=BC/AB
4. cosecant A =1/sin A= hypotenuse / side opposite to angle A =AC/BC
5. Secant A=1/Cas A= hypotenuse /side adjacent to angle A =AC/AB
6. cotangent A = 1/tan A=side adjacent to angle A/side opposite to angle A=AB/BC
Note: We have six trigonometric ratios and the reciprocal relations between them are as below
1) sin A x cosec A=1=> cosec A =1/sin A ; Sin A= 1/cosec A
2) cos A x sec A=1 => sec A = 1/cos A ; cos A = 1/sec A .
3) tan A x cot A= 1 => cot A = 1/tan A ; tan A=1/cot A
• Quotient relation:
1. tan A = sin A/cas A= sec A / cosec A
2. cot A = cas A/sin A= cosec A / sec A













This is one of the best blogs I've come across recently to learn maths. I appreciate the author's efforts in writing these educational articles. Find chemistry Edexcel Past Papers Maths.
ReplyDelete